Single-Tube vs Dual-Tube Coriolis Mass Flow Meters Explained
Coriolis mass flow meters are widely recognized as one of the most accurate flow measurement technologies available today. By directly measuring mass flow rather than volume, they eliminate the need for temperature or pressure compensation and deliver exceptional precision across a wide range of fluids.
Within Coriolis technology, however, single-tube and dual-tube designs represent two fundamentally different engineering approaches. Each has distinct structural characteristics, performance advantages, and ideal application scenarios. Understanding the differences between single-tube vs dual-tube Coriolis mass flow meters is essential for selecting the right instrument for your process.
This article provides a comprehensive comparison, covering working principles, accuracy, pressure drop, installation, vibration sensitivity, cost, and application suitability, helping you make an informed decision.
1. Overview of Coriolis Mass Flow Meter Technology
Before comparing tube configurations, it is useful to briefly understand how Coriolis mass flow meters work.
A Coriolis meter measures mass flow by detecting the Coriolis force, which occurs when a fluid flows through a vibrating tube. As the fluid moves, it causes a phase shift or twist in the tube proportional to the mass flow rate. Sensors measure this deflection, and the transmitter converts it into precise mass flow data.
In addition to mass flow, Coriolis meters can simultaneously measure:
-
Fluid density
-
Temperature
-
Volumetric flow (calculated)
The tube design—single or dual—plays a crucial role in how these measurements are generated and stabilized.
2. What Is a Single-Tube Coriolis Mass Flow Meter?
A single-tube Coriolis mass flow meter uses one continuous flow tube, typically curved or straight, which is excited into vibration by a drive system. Sensors positioned along the tube detect changes in vibration caused by fluid movement.
Key Structural Characteristics
-
One flow tube only
-
Compact mechanical structure
-
Smaller internal volume
-
Reduced material usage
Single-tube meters are often chosen where space constraints, low flow rates, or minimal pressure drop are critical.
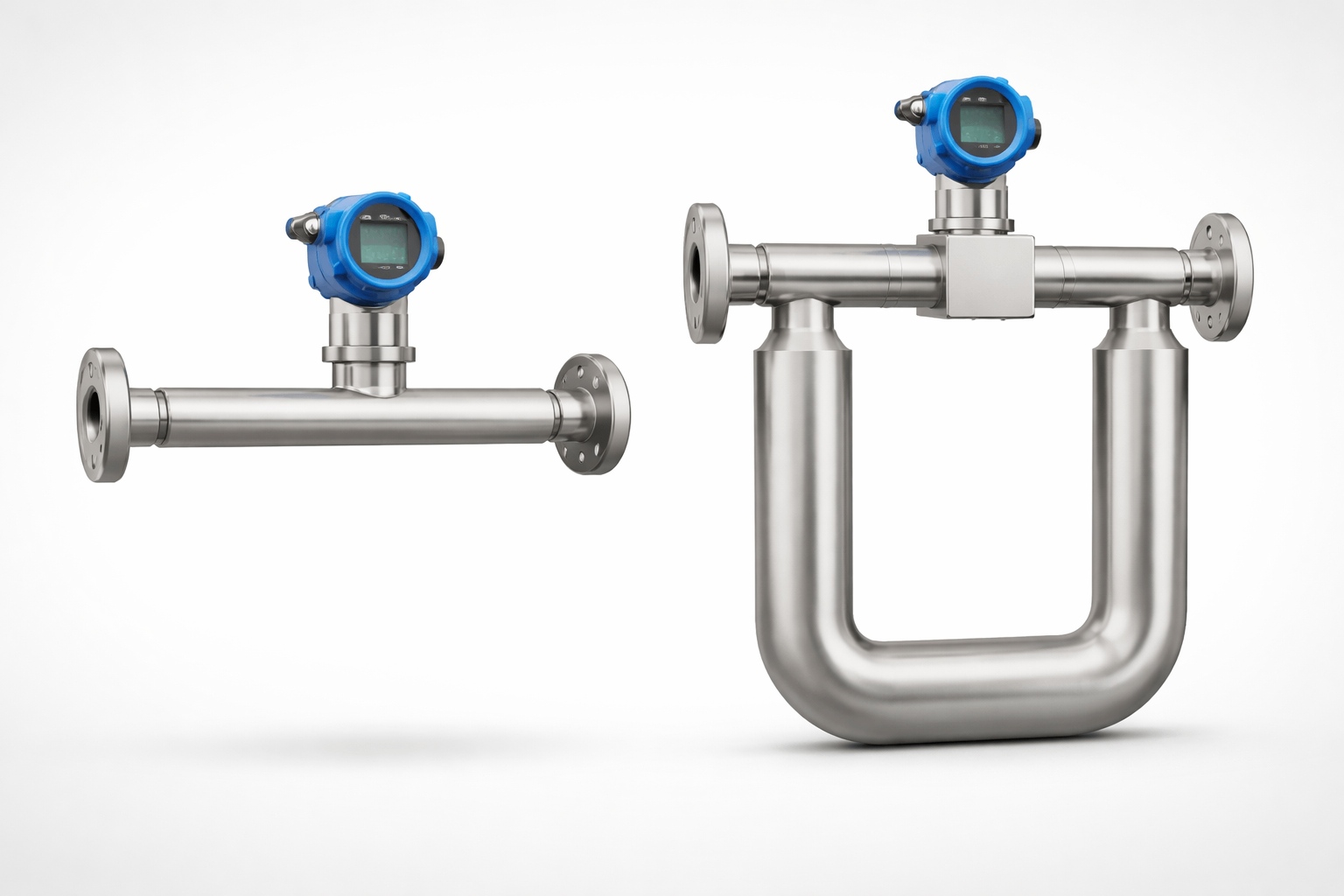
3. What Is a Dual-Tube Coriolis Mass Flow Meter?
A dual-tube Coriolis mass flow meter uses two identical tubes, usually arranged symmetrically. The tubes vibrate in opposite directions, and the Coriolis forces generated by flowing fluid create measurable phase shifts between the two tubes.
Key Structural Characteristics
-
Two parallel flow tubes
-
Symmetrical mechanical design
-
Self-balancing vibration structure
-
Higher rigidity and stability
Dual-tube meters are the most common Coriolis design in industrial environments due to their robustness and measurement consistency.
4. Working Principle Differences: Single vs Dual Tube
Although both designs rely on Coriolis force, the mechanical behavior differs significantly.
Single-Tube Design
-
Vibration occurs in one tube only
-
External forces (pump vibration, pipe stress) directly affect the tube
-
Signal processing relies heavily on digital filtering
Dual-Tube Design
-
Tubes vibrate in opposite directions
-
External vibrations tend to cancel out
-
More stable phase measurement
This fundamental difference explains many of the performance distinctions between the two types.
5. Accuracy and Measurement Stability
Dual-Tube Accuracy Advantage
Dual-tube Coriolis meters generally offer higher accuracy, especially under challenging conditions. Typical performance includes:
-
Mass flow accuracy as high as ±0.1%
-
Excellent repeatability
-
Strong resistance to flow disturbances
The symmetrical structure minimizes noise and improves long-term stability.
Single-Tube Accuracy Characteristics
Single-tube meters can still achieve high accuracy, particularly in:
-
Low flow applications
-
Clean, stable process conditions
However, they may be more sensitive to:
-
External vibration
-
Mechanical stress
-
Rapid process changes
In environments with strong mechanical interference, dual-tube designs usually outperform single-tube models.
6. Pressure Drop and Energy Efficiency
Pressure drop is a critical consideration in many systems.
Single-Tube Pressure Drop
-
Often lower pressure drop due to simpler flow path
-
Suitable for low-pressure systems
-
Ideal for dosing and batching
Dual-Tube Pressure Drop
-
Slightly higher pressure drop in many designs
-
Still significantly lower than many traditional flow meters
-
Acceptable for most industrial processes
When pressure loss must be minimized at all costs, single-tube meters may have an advantage.
7. Flow Range and Fluid Compatibility
Flow Range
-
Dual-tube meters typically support a wider flow range and higher maximum flow rates
-
Single-tube meters are commonly used for micro-flow and low-flow measurement
Fluid Types
Both designs handle:
-
Liquids and gases
-
High-viscosity fluids
-
Slurries (with appropriate design)
However, dual-tube meters often perform better with:
-
Two-phase flow
-
Density fluctuations
-
Harsh industrial fluids
8. Installation and Space Requirements
Single-Tube Installation
-
Compact and lightweight
-
Easier to install in confined spaces
-
Lower structural load on piping
Dual-Tube Installation
-
Larger footprint
-
Heavier construction
-
Requires stronger pipe support
In skid-mounted systems or laboratory environments, single-tube meters are often preferred due to their small size.
9. Resistance to External Vibration
This is one of the most critical differentiators.
Dual-Tube Superiority
The opposing vibration of dual tubes naturally cancels external mechanical noise. This makes dual-tube Coriolis meters:
-
Highly resistant to pump vibration
-
Reliable in heavy industrial environments
-
Stable in outdoor installations
Single-Tube Sensitivity
Single-tube meters:
-
Are more sensitive to external vibration
-
May require vibration isolation
-
Perform best in controlled environments
For installations near compressors, mixers, or rotating equipment, dual-tube designs are generally safer.
10. Maintenance and Long-Term Reliability
Dual-Tube Durability
-
Balanced stress distribution
-
Lower fatigue risk
-
Longer service life in harsh conditions
Single-Tube Maintenance
-
Simpler structure
-
Fewer components
-
Potentially easier to service
In high-cycle or high-stress applications, dual-tube meters often demonstrate superior long-term reliability.
11. Cost Considerations
Initial Cost
-
Single-tube Coriolis meters are usually less expensive
-
Dual-tube meters have higher upfront cost due to complex construction
Total Cost of Ownership
When considering:
-
Reduced downtime
-
Higher measurement confidence
-
Lower recalibration frequency
Dual-tube meters may offer better long-term value, especially in continuous production environments.
12. Typical Applications for Each Design
Best Applications for Single-Tube Coriolis Mass Flow Meters
-
Laboratory and pilot plants
-
Chemical dosing systems
-
Low-flow measurement
-
Skid-mounted equipment
-
Cost-sensitive projects
Best Applications for Dual-Tube Coriolis Mass Flow Meters
-
Chemical processing plants
-
Oil and gas production
-
Food and beverage manufacturing
-
Pharmaceutical production
-
High-vibration industrial environments
13. Selection Guidelines: How to Choose
When deciding between single-tube vs dual-tube Coriolis mass flow meters, consider the following:
-
Process Stability – Unstable processes favor dual-tube designs
-
Vibration Level – High vibration requires dual-tube meters
-
Flow Rate – Micro-flow favors single-tube; wide range favors dual-tube
-
Space Constraints – Limited space favors single-tube
-
Budget – Tight budgets may favor single-tube initially
-
Accuracy Requirements – Critical measurements favor dual-tube
14. Future Trends in Coriolis Tube Design
Advancements in sensor technology, digital signal processing, and materials science are narrowing the performance gap between single-tube and dual-tube designs. Modern single-tube meters are becoming more vibration-resistant, while dual-tube meters are being optimized for reduced pressure drop and compactness.
As Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing evolve, both designs will continue to coexist, serving different segments of the market.
15. Conclusion
The debate between single-tube vs dual-tube Coriolis mass flow meters is not about which technology is universally better, but rather which is better suited for a specific application.
-
Single-tube Coriolis meters excel in compact, low-flow, cost-sensitive, and space-limited applications.
-
Dual-tube Coriolis meters dominate in demanding industrial environments where accuracy, stability, and vibration resistance are critical.
By understanding the structural, performance, and economic differences outlined in this article, engineers and decision-makers can confidently select the Coriolis mass flow meter that delivers optimal performance and long-term value for their process.
Accura, as a professional Coriolis mass flow meter manufacturer, provides both single-tube and dual-tube solutions designed for high-precision mass flow measurement. With expertise in industrial flow metering, Accura ensures superior accuracy, vibration resistance, and reliable performance across a wide range of applications, including chemical processing, food and beverage production, and oil & gas operations. Whether you require compact, low-flow single-tube meters or robust dual-tube meters for demanding environments, Accura delivers innovative, durable, and cost-effective solutions tailored to your process needs.
www.accurainstrument.com
accurainstrument
Post Comment